Kedro architecture overview¶
There are different ways to leverage Kedro in your work, you can:
Commit to using all of Kedro (framework, project, starters and library); which is preferable to take advantage of the full value proposition of Kedro
You can use parts of Kedro, like the DataCatalog (I/O), OmegaConfigLoader, Pipelines and Runner, by using it as a Python library; this best supports a workflow where you don’t want to adopt the Kedro project template
Or, you can develop extensions for Kedro e.g. custom starters, plugins, Hooks and more
At a high level, Kedro consists of five main parts:
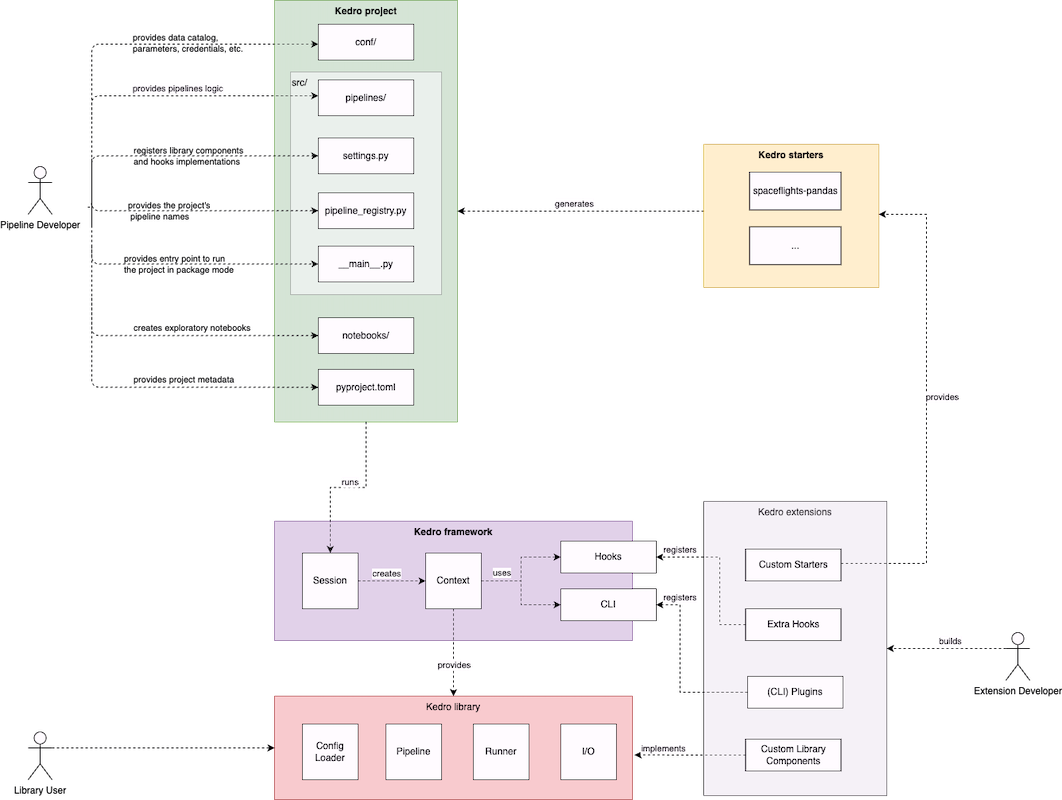
Kedro project¶
As a data pipeline developer, you will interact with a Kedro project, which consists of:
The
conf/directory, which contains configuration for the project, such as data catalog configuration, parameters, etc.The
srcdirectory, which contains the source code for the project, including:The
pipelinesdirectory, which contains the source code for your pipelines.settings.pyfile contains the settings for the project, such as library component registration, custom hooks registration, etc. All the available settings are listed and explained in the project settings chapter.pipeline_registry.pyfile defines the project pipelines, i.e. pipelines that can be run usingkedro run --pipeline.__main__.pyfile serves as the main entry point of the project in package mode.
pyproject.tomlidentifies the project root by providing project metadata, including:package_name: A valid Python package name for your project package.project_name: A human readable name for your project.kedro_init_version: Kedro version with which the project was generated.
Kedro framework¶
Kedro framework serves as the interface between a Kedro project and Kedro library components. The major building blocks of the Kedro framework include:
Sessionis responsible for managing the lifecycle of a Kedro run.Contextholds the configuration and Kedro’s main functionality, and also serves as the main entry point for interactions with core library components.Hooksdefines all hook specifications available to extend Kedro.CLIdefines built-in Kedro CLI commands and utilities to load custom CLI commands from plugins.
Kedro starter¶
You can use a Kedro starter to generate a Kedro project that contains boilerplate code. We maintain a set of official starters but you can also use a custom starter of your choice.
Kedro library¶
Kedro library consists of independent units, each responsible for one aspect of computation in a data pipeline:
OmegaConfigLoaderprovides utility to parse and load configuration defined in a Kedro project.Pipelineprovides a collection of abstractions to model data pipelines.Runnerprovides an abstraction for different execution strategy of a data pipeline.I/Oprovides a collection of abstractions to handle I/O in a project, includingDataCatalogand manyDatasetimplementations.
Kedro extension¶
You can also extend Kedro behaviour in your project using a Kedro extension, which can be a custom starter, a Python library with extra hooks implementations, extra CLI commands such as Kedro-Viz or a custom library component implementation.
If you create a Kedro extension, we welcome all kinds of contributions. Check out our guide to contributing to Kedro. Dataset contributions to kedro-datasets are the most frequently accepted, since they do not require any changes to the framework itself. However, we do not discourage contributions to any of the other kedro-plugins.